‘Does Turnitin detect paraphrasing?’ is a common question you’ll find thrown out there by students across social media communities focusing on matters of students and education. While Turnitin is good at spotting exact matches and copied text, it’s less straightforward with paraphrasing. If you reword something from another source but keep the same structure or ideas, Turnitin might still flag it for review, depending on how closely it resembles the original.
While Turnitin is a powerful tool in detecting plagiarism, a high percentage of students assume that rewording their written content will easily bypass detection by Turnitin. However, the technology behind Turnitin can still identify similarities in sentence structure, ideas, and phrasing. It is important to understand how Turnitin detects paraphrasing to ensure that you’re not unintentionally flagged for plagiarism, even if you think you’ve rephrased something the right way.
What is Turnitin, and how does it work?

Turnitin is a tool that has been around for over 25 years, with its primary job being checking for plagiarism in academic work. Let’s demonstrate using an example. If, for instance, you copy a paragraph from a website without citing it properly, Turnitin will highlight the section and show the source where it came from. Even if you only change a few words, Turnitin can still flag it if the structure or meaning remains too close to the original.
How does Turnitin analyze content?
Turnitin has a database that includes academic papers, web content, and published research papers & books. Using a text-matching algorithm, Turnitin scans through and compares the submitted work to its database. Turner then searches for patterns, phrases, and sequences of words similar to the content already available in its database. A good example is if a student copies content from an online article and submits it as their own, Turnitin will recognize that the wording matches closely with an existing source and mark it for review. Below is a detailed overview of Turnitins database;
- Academic papers include a collection of previously submitted schoolwork from universities and colleges from all over the world.
- Web content includes published articles, news articles, blogs, and other materials on the web.
Can Turnitin Detect Paraphrasing?
Let’s answer this question using an example.
If you directly copy a sentence like, “Global warming is caused by the increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere” from a website, Turnitin will highlight this as a match and show you the source. Even if you would rephrase it to, “The rise in greenhouse gases leads to global warming,” Turnitin might still flag it because the idea and structure are similar to the original, even though the words are slightly different.
Even when the wording is adjusted to something different, the underlying meaning, sequence of arguments, or structure of the text may still closely resemble the original content copied from somewhere, which would then trigger a similarity match.
The ability of Turnitin to detect paraphrasing lies in how well the paraphrasing is done. Turnitin might struggle to detect well-done paraphrasing where the ideas are restated in a completely different way. However, if the meaning or structure stays too close to the original, the chances of being detected remain high.
Does paraphrasing confuse Turnitin?
Let’s look at some examples of paraphrased sentences that may or may not be detected by Turnitin.
Examples of Paraphrased Sentences
1. An example that may be detected by Turnitin:
- Original: “Technological advancements have greatly improved communication across the globe.”
- Paraphrased sentence: “Improvements in technology have significantly enhanced global communication.”
- Why Turnitin may detect it: The structure is nearly the same, while key phrases such as “improvements” and “global communication” remain the same.
An example that may not be detected by Turnitin:
- Original: “Technological advancements have greatly improved communication across the globe.”
- Paraphrased sentence: “New technologies have revolutionized how people communicate worldwide.”
- Why Turnitin may not detect it: New words have been incorporated, e.g., ‘from across the globe to worldwide’. The sentence has been rephrased with a different structure too, making it harder for Turnitin to detect the paraphrasing.
2. Example that may be detected by Turnitin:
- Original: “Deforestation contributes significantly to the loss of biodiversity.”
- Paraphrased: “Biodiversity loss is significantly impacted by deforestation.”
- Why it may be detected: The sentence has just been rearranged with the same core meaning and key terms.
An example that may not be detected by Turnitin:
- Original: “Deforestation contributes significantly to the loss of biodiversity.”
- Paraphrased: “The clearing of forests plays a major role in reducing the variety of species in ecosystems.”
- Why it may not be detected: The wording has been changed substantially, using different phrases and synonyms, making it harder for Turnitin to detect the paraphrasing.
These examples show how Turnitin relies on similarities in structure, phrasing, and key terms, but well-done paraphrasing can somehow escape detection.
How Turnitin Detects Similarities in Paraphrasing
Turnitin doesn’t only look for exact matches but also considers patterns in ideas, sentence structures, and important terms. When you paraphrase, if your content keeps these things too close to the original, Turnitin might see it as a similarity.
Here’s how that works:
Same sentence structure with different words:
Even if you change some words but keep the sentence in the same order, Turnitin can still detect the paraphrasing. Let’s study the example below:
- Original: “The invention of the internet revolutionized global communication.”
- Paraphrased sentence: “The creation of the internet transformed worldwide communication.”
- Why the similarity may be detected: The sentence structure and meaning remain almost the same, with only minor word changes.
Key terms repeated in similar ways:
If important words like specific names, technical terms, or uncommon phrases appear in the same order as the original, Turnitin may pick up on that. See the below example:
- Original: “Photosynthesis converts sunlight into chemical energy, providing food for plants.”
- Paraphrased sentence: “Photosynthesis transforms sunlight into chemical energy, supplying nutrition to plants.”
- Why Turnitin might detect paraphrasing: The key terms (“photosynthesis,” “sunlight,” “chemical energy”) are repeated in a very similar format.
Keeping the same ideas or points in the same order:
Even if you completely rephrase sentences, Turnitin might flag your work if the main ideas or argument points follow the same order as the original source. See the below example:
- Original: “First, climate change causes extreme weather events. Then, it leads to rising sea levels and finally, disrupts agriculture.”
- Paraphrased sentence: “Initially, climate change triggers severe weather. Afterward, it results in higher sea levels and ultimately affects farming.”
- Why Turnitin might detect paraphrasing: Though the wording is different, the order of ideas is exactly the same as that of the original.
Common phrases or collocations:
Certain phrases are common in academic writing, and using them in the same context as another source can lead to them being similar. See the below example:
- Original: “The results of the study suggest a significant correlation between diet and mental health.”
- Paraphrased sentence: “The findings of the research indicate a strong link between nutrition and mental health.”
- Why Turnitin might detect paraphrasing: “significant correlation” and “strong link” are common ways to phrase the same idea, so the similarity might still be detected by Turnitin.
In summary, Turnitin knows paraphrased content when it scans and finds similarities in the structure, phrasing, or key terms of the content. Simply swapping words is not enough; changing the overall structure and rephrasing ideas in new ways can help the paraphrasing not to be detected by Turnitin.
How to Paraphrase Properly Without Being Detected by Turnitin
To avoid paraphrasing detection by Turnitin, you need to completely rephrase ideas in a new way rather than just interchanging words. You should also understand the original text well enough to rewrite the concept in your own words. Here’s how to do it effectively:
Change the sentence structure:
You should not just change words. Make sure to rearrange how the information is presented and use a different sentence pattern or structure. Here is an example:
- Original: “Climate change causes rising sea levels, which endanger coastal cities.”
- properly paraphrased sentence: “Coastal cities are at greater risk as sea levels rise, a result of ongoing climate change.”
- Why it works: The sentence structure has been altered, and different phrasing is used while it keeps the original meaning.
Use synonyms for key terms (where appropriate):
Replace words with synonyms, but make sure they fit the context.
Example:
- Original: “The rapid expansion of technology is transforming the global economy.”
- Paraphrased sentence: “The swift growth of technology is reshaping the world economy.”
- Why this works: Synonyms like “rapid” a” and “transforming” to “reshaping” have been used, and the phrasing has changed.
Break down complex ideas into simpler parts:
If the original text is detailed or complex, explain it in simpler terms using your own words. This not only changes the structure but also makes the idea clearer.
Example:
- Original: “Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.”
- Paraphrased sentence: “Plants use photosynthesis to turn sunlight into energy, which is stored in sugars like glucose.”
- Why this works: The idea is explained in simpler terms with different wording, yet the core meaning remains the same.
Summarize the main idea:
Instead of paraphrasing sentence by sentence, try to summarize the overall meaning or the main idea. This helps to avoid using too many similar phrases or structures.
Example:
- Original: “The study found that regular exercise reduces stress levels by improving mood and mental health.”
- Paraphrased sentence: “The research concluded that exercising frequently can lower stress and boost mental well-being.”
- Why this works: The key idea is summarized in new words with a different sentence structure.
Use a different order of information:
Change the sequence of how the information is presented. This makes your paraphrase less likely to resemble the original.
Example:
- Original: “The economy benefits from technological innovation because it leads to job creation and boosts productivity.”
- Paraphrased sentence: “By creating jobs and enhancing productivity, technological innovation greatly supports the economy.”
- Why this works: The order of information has been flipped, and the wording has been adjusted, which makes the paraphrased sentence unique
By focusing on changing the structure, wording, and presentation of ideas, you can paraphrase effectively without having trouble with Turnitin.
What is the acceptable percentage for Turnitin?
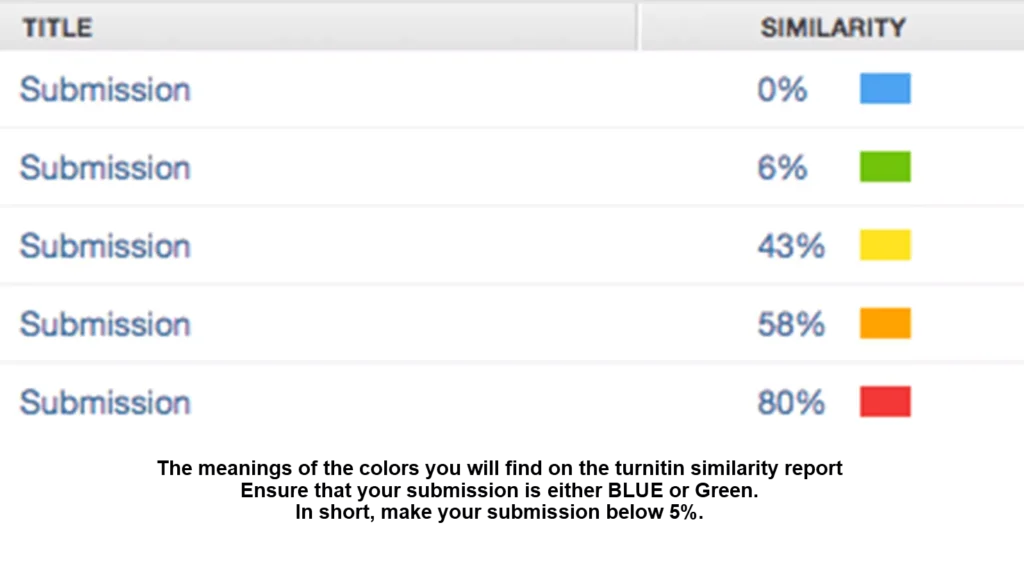
Is 30% OK on Turnitin? Is 50% high on Turnitin? Is a 20% Turnitin score okay? Is 5% on Turnitin bad?
What percentage is too low for Turnitin? You will find all these types of questions everywhere. Turner doesn’t have a universally set acceptable percentage for all submissions. The similarity score simply measures how much of your submission matches other sources. It’s up to your institution or instructor to define what percentage is acceptable.
Typically:
- A green score (1-24%) often suggests a safe level with minimal matching content.
- A yellow score (25-49%) or above may require a closer look, especially if the assignment involves too much quoting without original input.
- Scores in orange (50–74%) or red (75–100%) are concerning, indicating significant portions of text match other sources, potentially signaling plagiarism.
Always follow your specific assignment or instructor’s guidelines to determine what’s acceptable, as some instructors might allow higher percentages depending on the nature of the work, such as research-heavy projects.
What happens if you get caught plagiarizing?
If a student is caught plagiarizing in college, there are several potential consequences of plagiarism which may vary depending on the institution
- Warning: If it’s a minor issue, you may get a warning or be asked to revise and resubmit the work.
- Grade Penalty: You might receive a lower grade or even fail the assignment.
- Academic Disciplinary Action: In serious cases, schools can take disciplinary action that may include probation, suspension, or even expulsion.
While Turnitin helps maintain academic honesty, if you get flagged for paraphrasing, it could have serious consequences. My advice is to always cite your sources properly and avoid relying on close paraphrasing too much.
Conclusion
Turnitin can detect paraphrasing, but it depends on how closely the paraphrased text resembles the source. If the changes are minimal, Turnitin will likely flag it as a match. The key thing is to ensure you properly cite your work and significantly rework the ideas in your own words while maintaining academic integrity. While Turnitin is a useful tool for identifying similarities, it is not a definitive measure of plagiarism on its own. Institutions use it to help students develop better writing habits, but ultimately, how you paraphrase and cite your sources will determine your success.